WHAT ARE COMMON CAUSES?
Foot and ankle pain can be caused by various conditions affecting the bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, or other structures in the foot and ankle region.
Foot Pain Symptoms:
- Pain: Persistent or intermittent pain in the foot is the primary symptom. The pain may vary in intensity and location, ranging from the toes to the heel or arch.
- Swelling: Inflammation of the foot or surrounding tissues can lead to visible swelling or puffiness.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the foot or ankle, with a reduced range of motion. The affected foot may feel stiff and may be accompanied by a feeling of tightness.
- Tenderness: The foot area may be tender to touch or pressure.
- Warmth: Inflammation in the foot may cause the area to feel warm to the touch.
- Redness: Inflammatory conditions may cause the skin around the foot to appear red.
- Weakness: A feeling of weakness in the foot, making it challenging to bear weight or walk properly.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations of pins and needles or loss of sensation in the foot, indicating possible nerve involvement.
- Difficulty Walking: Foot pain may affect walking, causing a limp or altered gait.
- Corns and Calluses: Areas of thickened skin may develop in response to pressure or friction.
- Blisters: Fluid-filled sacs may form on the skin due to irritation or friction.
Ankle Pain Symptoms:
- Pain: Persistent or intermittent pain in the ankle is the primary symptom. The pain may vary in intensity and may be dull, aching, sharp, or throbbing in nature.
- Swelling: Inflammation of the ankle joint or surrounding tissues can lead to visible swelling or puffiness.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the ankle, with a reduced range of motion. The ankle may feel stiff and may be accompanied by a feeling of tightness.
- Tenderness: The ankle area may be tender to touch or pressure.
- Bruising: Injuries or trauma to the ankle may cause bruising or discoloration of the skin.
- Instability: A feeling of instability or giving way in the ankle, indicating possible ligament or tendon damage.
- Locking: The ankle joint may feel like it gets “locked” or stuck in a certain position during movement.
- Difficulty Walking: Ankle pain may affect walking, causing a limp or altered gait.
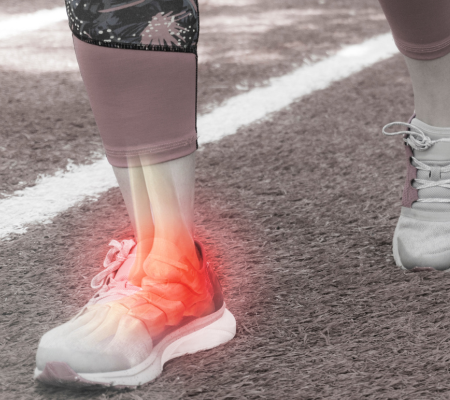
COMMON CAUSES FOR FOOT & ANKLE PAIN?
- Plantar Fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot.
- Achilles Tendinitis: Inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
- Ankle Sprains: Overstretching or tearing of ligaments in the ankle due to twisting or rolling the foot.
- Stress Fractures: Small cracks in the bones of the foot or ankle, often caused by overuse or repetitive impact.
- Bunions: A bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of the big toe.
- Gout: A form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, including the foot and ankle.
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the tibial nerve as it passes through the tarsal tunnel, causing pain and tingling in the foot.
- Plantar Warts: Viral infections that cause small, painful growths on the soles of the feet.
If you experience persistent or severe foot and ankle pain or any accompanying symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation from a healthcare professional. Proper diagnosis is crucial to determine the underlying cause of the pain and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Treatment options may include rest, physical therapy, pain medication, orthotics, corticosteroid injections, or in some cases, surgery, depending on the specific condition and individual needs.
COMMON DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT?
Diagnosis
Diagnosis and treatment for foot pain involve a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional to identify the underlying cause of the pain. Here’s a general outline of the common diagnosis and treatment steps for foot pain:
- Medical History: The healthcare provider will inquire about the nature of the foot pain, its location, duration, aggravating and alleviating factors, and any previous injuries or medical conditions.
- Physical Examination: A comprehensive examination of the foot will be conducted to assess any visible abnormalities, tenderness, swelling, range of motion, and signs of inflammation.
- Gait Analysis: The way you walk (gait) may be assessed to identify any issues with foot mechanics that could contribute to foot pain.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays can provide images of the bones in the foot, helping identify conditions such as fractures, arthritis, or bone abnormalities. MRI or CT scans may be used to visualize soft tissues like ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests may be ordered to rule out certain medical conditions that could contribute to foot pain.
Treatment
The treatment approach for foot pain depends on the specific diagnosis and severity of the condition. Common treatment options include:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that worsen the pain and giving the foot time to rest can promote healing.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom-made shoe inserts (orthotics) or supportive footwear can help improve foot mechanics and alleviate pain caused by abnormal foot alignment.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design exercises and stretches to strengthen the foot muscles, improve flexibility, and correct gait abnormalities.
- Pain Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of severe inflammation or pain, corticosteroid injections may be administered to provide temporary relief.
- Cold and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs to reduce inflammation and swelling or using heat therapy to relax the muscles can be beneficial.
- Footwear Modification: Wearing shoes that provide proper support and cushioning can be helpful, especially for conditions like plantar fasciitis.
- Padding and Strapping: Padding or strapping the foot can help redistribute pressure and protect sensitive areas.
- Night Splints: For conditions like plantar fasciitis, wearing night splints can help stretch the foot and reduce morning pain.
- Weight Management: For individuals with excess body weight, weight loss can alleviate pressure on the feet and reduce pain.
- Physical Modalities: Other therapies such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or traction may be utilized to reduce pain and promote healing.
- Surgery: In cases of severe injuries, advanced arthritis, or conditions that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgery may be considered. Procedures may involve removing bone spurs, repairing tendons, or fusing joints.
There are several surgical procedures for foot and ankle conditions, each designed to address specific issues and provide relief from pain or improve function. Here is a list of common surgical procedures for the foot and ankle:
- Ankle Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure using a small camera (arthroscope) to visualize and treat various ankle problems, such as cartilage damage, loose bodies, or ankle impingement.
- Ankle Ligament Reconstruction: A surgery to repair or reconstruct damaged ligaments in the ankle, often performed for chronic ankle instability.
- Ankle Fusion (Ankle Arthrodesis): A surgery to fuse the bones of the ankle joint, often performed to treat severe arthritis or ankle deformities.
- Ankle Replacement (Ankle Arthroplasty): A procedure to replace the damaged ankle joint with an artificial joint made of metal and plastic components.
- Bunionectomy: A surgery to remove a bunion, a bony bump that forms at the base of the big toe.
- Hammer Toe Correction: A procedure to straighten a hammer toe, where the toe is bent at the middle joint.
- Achilles Tendon Repair or Reconstruction: A surgery to repair or reconstruct a torn or damaged Achilles tendon.
- Tarsal Tunnel Release: A procedure to release the tibial nerve from compression in the tarsal tunnel, similar to carpal tunnel release in the wrist.
- Flatfoot Correction (Tendon Transfer or Osteotomy): Surgical procedures to correct flatfoot deformities, often involving tendon transfers or bone realignment.
- Plantar Fascia Release: A surgery to release the plantar fascia to treat chronic plantar fasciitis.
- Calcaneal Osteotomy: A procedure to reposition the heel bone (calcaneus) to correct deformities and improve foot alignment.
- Metatarsal Osteotomy: A surgery to reposition or shorten one or more metatarsal bones to treat various forefoot conditions.
- Tendon Repair or Reconstruction (e.g., Peroneal Tendon Repair): A surgery to repair or reconstruct damaged tendons in the foot and ankle.
- Ankle Fracture Fixation: A surgery to stabilize fractured bones in the ankle using plates, screws, or other fixation devices.
- Ankle Fusion (Tibiotalar Fusion): A surgery to fuse the tibia (shinbone) with the talus bone in the ankle joint, often performed for severe arthritis.
- Lateral Ankle Stabilization: A procedure to reconstruct the lateral ankle ligaments to treat chronic ankle sprains.
Please note that the appropriateness of these surgical procedures depends on the individual’s specific foot and ankle condition, symptoms, and the expertise of the orthopedic surgeon. Non-surgical treatments, such as physical therapy or medications, are often considered as the first line of management for many foot and ankle conditions, and surgery is typically reserved for cases where conservative measures have not provided adequate relief or for more severe conditions. Always consult with an orthopedic specialist to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific foot or ankle condition.
The treatment plan will be tailored to each individual’s specific needs and condition. It’s crucial to follow the guidance of your orthopedic specialist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment to effectively manage foot pain and facilitate a successful recovery

S. EVAN CARSTENSEN, M.D.
ORTHOPEDIC SPECIALIST
Board certified, fellowship trained orthopaedic shoulder, knee, hip, and sports medicine specialist managing injuries both non-operatively and operatively by specifically utilizing evidence-based medicine and minimally invasive techniques.

DARYL DYKES, M.D.
ORTHOPEDIC SPECIALIST
Board certified orthopedic surgeon with extensive experience in diagnosis, treatment and management of spine, bone or joint condition, and specializes in reconstruction of the shoulder, hip, and knee, including total joint replacement.

LLOYD JOHNSON, M.D.
ORTHOPEDIC SPECIALIST
Board-certified and fellowship-trained in both reconstructive and spine surgery with extensive experience in the management of complex conditions, diagnosis and treatment of:general orthopedics, spine disorders, sports medicine, orthopedic upper and lower extremities.

LOY VAUGHAN, M.D.
ORTHOPEDIC SPECIALIST
General orthopedic surgeon treating musculoskeletal condition with a particular interest in shoulder, hip, and knee joint replacement, shoulder and knee arthroscopy, and fracture care. Dr. Vaughan is a board-eligible orthopedic surgeon with experience in complex conditions, treatment and management.

