Stress fractures are small cracks or breaks in the bones that occur due to repetitive stress or overuse. When it comes to stress fractures in the foot or ankle, proper treatment is essential to promote healing and prevent further damage. Here’s some information about the treatment of stress fractures in the foot or ankle:
1. Rest:
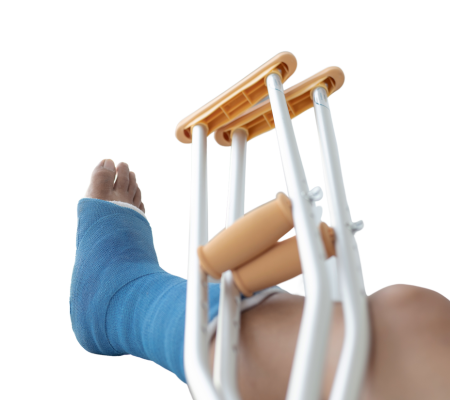
Rest is crucial for allowing the bones to heal. You may need to limit weight-bearing activities and avoid high-impact exercises or activities that aggravate the fracture site. Crutches or a walking boot may be recommended to offload the affected foot or ankle.
2. Immobilization:
Immobilizing the foot or ankle can help promote healing by reducing stress on the fractured bone. Your doctor may recommend a walking boot, cast, or brace to immobilize the area.
3. Ice Therapy:
Applying ice packs to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation. Use ice for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
4. Pain Management:
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. However, it’s important to follow the instructions and consult with your healthcare provider before taking any medication.
5. Gradual Return to Activity:
Once the bone has healed, a gradual return to weight-bearing activities and exercises is typically recommended. This should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional or physical therapist to avoid reinjury.
6. Orthotic Devices:
Your doctor may prescribe custom orthotic inserts or footwear modifications to provide support, cushioning, and proper alignment of the foot and ankle. These can help alleviate pressure on the fractured bone and prevent future stress fractures.
7. Physical Therapy:
Depending on the severity and location of the stress fracture, physical therapy may be recommended. Physical therapists can guide you through exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and balance, as well as help you gradually return to your regular activities.
8. Follow-up and Monitoring:
Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider will ensure that the stress fracture is healing properly. X-rays or other imaging tests may be performed to monitor the progress.
In some cases, if the stress fracture is severe, doesn’t heal with conservative measures, or there is a risk of complications, surgery may be required to stabilize the bone or remove damaged tissue. However, surgery is not commonly needed for most stress fractures.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as an orthopedic specialist or a podiatrist, for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for stress fractures in the foot or ankle. They can assess the severity of the fracture and provide personalized recommendations for your specific situation. At Alabama Bone and Joint Clinic our specialists are able to guide you through your treatment options. Call today to schedule an appointment with one of our experts in orthopedic care.
My visit to AL Bone and Joint Clinic was s pleasant visit , wait time was minimal the staff were friendly and knowledgeable. The Dr explained my injury so I could understand . They made me feel comfortable and taken care of.
CEO
I have been seeing Dr. Johnson at Alabama Bone & Joint for a few years now. He has always been professional, knowledgeable and very understanding. He takes time to answer questions and provide as much information as possible to ensure I understand what is going on and what the next steps should be. The staff is always kind and amazing. His nurse Heather is my favorite, she always has a smile and is very caring. I highly recommend.
CEO
Very pleasant experience. Very helpful, provided all answers to questions and information that was needed
CEO
Previous
Next

