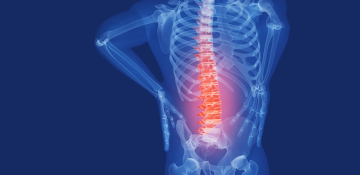
Lumbar spine disease
Lumbar spine disease refers to various medical conditions that affect the lumbar spine, which is the lower portion of the spine located in the lower back. The lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae (L1-L5) and is responsible for supporting the upper body, providing stability, and facilitating movement.
Here are some common lumbar spine diseases:
Lumbar Disc Herniation:
Lumbar disc herniation occurs when the intervertebral discs in the lumbar spine bulge or rupture, causing compression of nearby nerves. This can lead to symptoms such as lower back pain, radiating leg pain (sciatica), numbness, tingling, and weakness in the legs.
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis:
Lumbar spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal in the lumbar spine, resulting in compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots. It is often caused by degenerative changes in the spine, such as arthritis, thickened ligaments, or bone spurs. Symptoms may include lower back pain, leg pain, numbness or weakness in the legs, and difficulties with walking or balance.
Lumbar Spondylolisthesis:
Lumbar spondylolisthesis refers to the forward displacement of one vertebra over the one below it. It can be caused by various factors, including degenerative changes, fractures, or congenital abnormalities. Symptoms may include lower back pain, stiffness, leg pain, and potential neurological symptoms if nerve compression occurs.
Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease:
Lumbar degenerative disc disease is a condition characterized by the gradual breakdown and degeneration of the intervertebral discs in the lumbar spine. This can lead to symptoms such as lower back pain, limited mobility, stiffness, and potential nerve compression if disc height loss occurs.
Lumbar Spinal Fractures:
Lumbar spinal fractures can result from trauma, osteoporosis, or underlying medical conditions. Fractures may involve the vertebral body or the processes of the vertebrae. Symptoms may include severe back pain, limited mobility, and potential nerve damage or spinal instability.
Treatment options for lumbar spine diseases depend on the specific condition, severity of symptoms, and individual factors. Non-surgical treatments may include pain management, physical therapy, exercise, and lifestyle modifications. In more severe cases or when conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical interventions such as spinal fusion, laminectomy, or discectomy may be considered.
If you are experiencing symptoms or have concerns related to lumbar spine disease, it is recommended to consult with a spine specialist or orthopedic surgeon. They will evaluate your specific condition, conduct diagnostic tests if needed, and recommend an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your needs.
As with any surgical procedure, ALIF carries risks and potential complications, including infection, bleeding, nerve or blood vessel injury, graft failure, or pseudarthrosis (failed fusion). Your surgeon will discuss these risks with you before the procedure and provide guidance on postoperative care and activity restrictions. At Alabama Bone and Joint Clinic our spine specialist will guide you through your treatment options. Call today to schedule an appointment with our expert in spine care, Winston Capel, M.D. is board certified in neurosurgery and fellowship trained in spinal surgery.
My visit to AL Bone and Joint Clinic was s pleasant visit , wait time was minimal the staff were friendly and knowledgeable. The Dr explained my injury so I could understand . They made me feel comfortable and taken care of.
CEO
I have been seeing Dr. Johnson at Alabama Bone & Joint for a few years now. He has always been professional, knowledgeable and very understanding. He takes time to answer questions and provide as much information as possible to ensure I understand what is going on and what the next steps should be. The staff is always kind and amazing. His nurse Heather is my favorite, she always has a smile and is very caring. I highly recommend.
CEO
Very pleasant experience. Very helpful, provided all answers to questions and information that was needed
CEO
Previous
Next

